Summary of Arduino Esp8266
The article introduces the ESP8266 WiFi serial transceiver module, a highly integrated SoC designed for wireless internet connectivity with minimal external circuitry. It features on-board processing, extensive GPIO support, and integrated TCP/IP stack, making it suitable for various IoT applications. The tutorial demonstrates controlling the ESP8266 using a Seeeduino to request a webpage via TCP socket. The module supports interfaces such as SDIO, SPI, UART, and provides integrated RF components, power management, and security features. Specifications highlight low power consumption, high output power, and Wi-Fi standards compliance.
Parts used in the Arduino Basic Wifi Project using ESP8266 wifi module:
- ESP8266 WiFi Serial Transceiver Module
- Seeeduino (Arduino Compatible Board)
Esp8266 Introduction:
This is WiFi serial transceiver module, based on ESP8266 SoC. ESP8266 module is a TTL “Serial to Wireless Internet” device. Providing your microcontroller has the ability to talk to a TTL serial device (most do) you’ll be in business. It is a highly integrated chip designed for the needs of a new connected world. It offers a complete and self-contained Wi-Fi networking solution, allowing it to either host the application or to offload all Wi-Fi networking functions from another application processor.
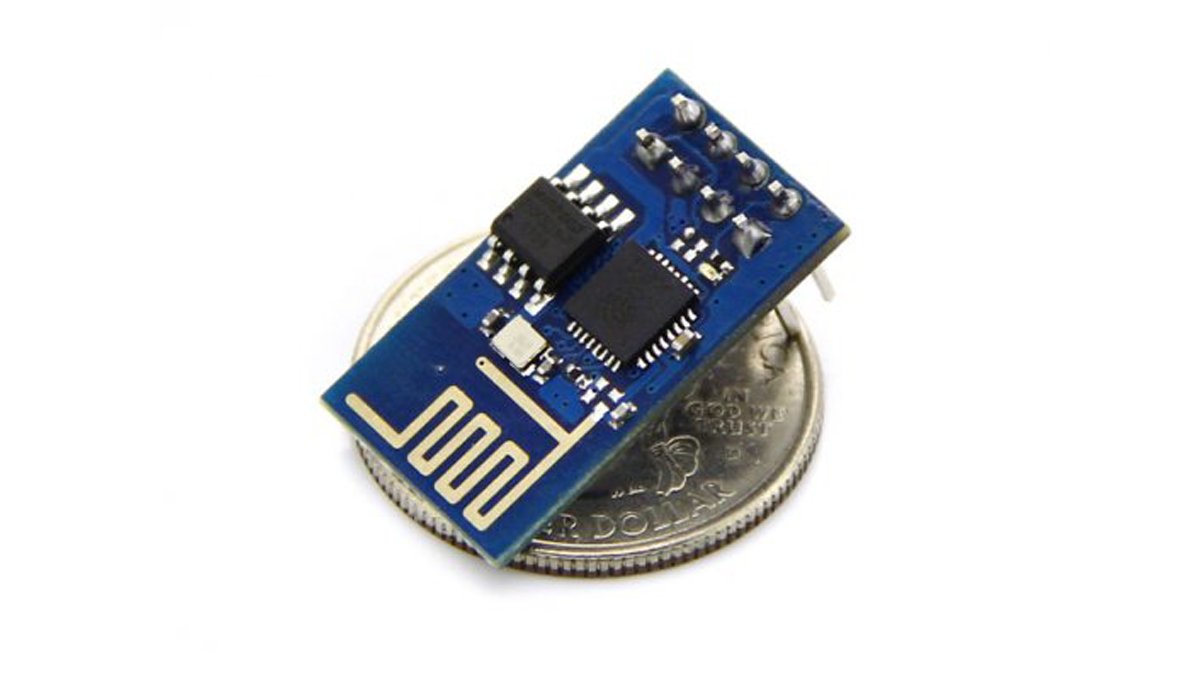

ESP8266 has powerful on-board processing and storage capabilities that allow it to be integrated with the sensors and other application specific devices through its GPIOs with minimal development up-front and minimal loading during runtime. Its high degree of on-chip integration allows for minimal external circuitry, and the entire solution, including front-end module, is designed to occupy minimal PCB area.
In this tutorial, we’ll use a seeeduino to control the ESP8266 WiFi module to request a static page from the internet. This is a basic use of TCP socket, for other usage, please refer to the AT command guide of the module.
The SOC has Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack
ESP8266 has powerful on-board processing and storage capabilities that allow it to be integrated with the sensors and other application specific devices through its GPIOs with minimal development up-front and minimal loading during runtime. Its high degree of on-chip integration allows for minimal external circuitry, and the entire solution, including front-end module, is designed to occupy minimal PCB area.
Esp8266 Specifications:
Corresponding Interface:
SDIO 2.0, SPI, UART
32-pin QFN package
Integrated RF switch, balun, 24dBm PA, DCXO, and PMU
Integrated RISC processor, on-chip memory and external memory interfaces
Integrated MAC/baseband processors
Quality of Service management
I2S interface for high fidelity audio applications
On-chip low-dropout linear regulators for all internal supplies
Proprietary spurious-free clock generation architecture
Integrated WEP, TKIP, AES, and WAPI engines
Specification:
802.11 b/g/n
Wi-Fi Direct (P2P), soft-AP
Integrated TCP/IP protocol stack
Integrated TR switch, balun, LNA, power amplifier and matching network
Integrated PLLs, regulators, DCXO and power management units
+19.5dBm output power in 802.11b mode
Power down leakage current of <10uA
Integrated low power 32-bit CPU could be used as application processor
SDIO 1.1/2.0, SPI, UART
STBC, 1×1 MIMO, 2×1 MIMO
A-MPDU & A-MSDU aggregation & 0.4ms guard interval
Wake up and transmit packets in < 2ms
Standby power consumption of < 1.0mW (DTIM3)