Summary of Arduino – Control a DC motor with TIP120, potentiometer and multiple power supplies
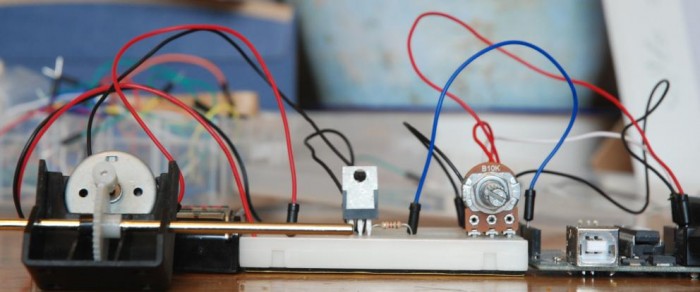
This article explains how to control the speed of a DC motor using a potentiometer connected to an Arduino, with a TIP120 transistor acting as a switch to handle higher current from an external power source. The TIP120 transistor controls current flow from the Arduino’s PWM pin to the motor. A diode is used for protection against power surges. The potentiometer adjusts the PWM signal, thereby regulating motor speed. Sharing a common ground between the Arduino and power supply is essential, and a 1k Ohm resistor is used to connect the Arduino pin to the transistor base.
Parts used in the TIP120 Arduino DC Motor Control Circuit:
- 1k Ohm resistor (Brown, Black, Red, Gold)
- 10k Potentiometer
- TIP120 Transistor
- 1N4004 1A Diode
- 6V DC Motor
- Arduino Duemilanove w/ ATMEGA328
- Breadboard / Prototyping board
- Jumper/Connector wires
- 4x AA battery holder
- 4x AA batteries
- Optional 9V DC power supply or USB power for Arduino
A simple diagram demonstrating how to regulate the velocity of a DC motor using a potentiometer connected to your Arduino device. Additionally demonstrates the method of utilizing a TIP120 transistor for enabling the Arduino to manage a more powerful power source.
Transistors consist of 3 pins, with the third pin (Base) enabling control of the current flowing through the other two pins (Collector and Emitter). In this tutorial, I am utilizing the electrical power from the Arduino’s Digital PWM pin 9 (+5V) to regulate the current flow to a DC motor, which requires a separate power source with a significantly higher current capacity than what the Arduino board is capable of providing or managing. Every transistor is specifically designed for a particular operating range or current, as is typical for electrical components.
Displayed below are the pins of TIP120 along with their representation in a schematic diagram:
That is the transistor. The next component is the rectifier diode, which I am placing between the power supply and the motor. It functions as a unidirectional gate to restrict current flow in one direction, ensuring my circuit remains safe in case of a power surge from the motor power supply or excessive current draw by the motor. The primary point is that like LED’s, diodes have a proper orientation indicated on the left.
Another component is the potentiometer, which functions as a resistor that can be adjusted. You can regulate the current by adjusting how much is allowed to pass through when you turn it. Like resistors, potentiometers also have a resistance rating in Ohms and a power rating. I am using a potentiometer with a resistance rating of 10K ohms.
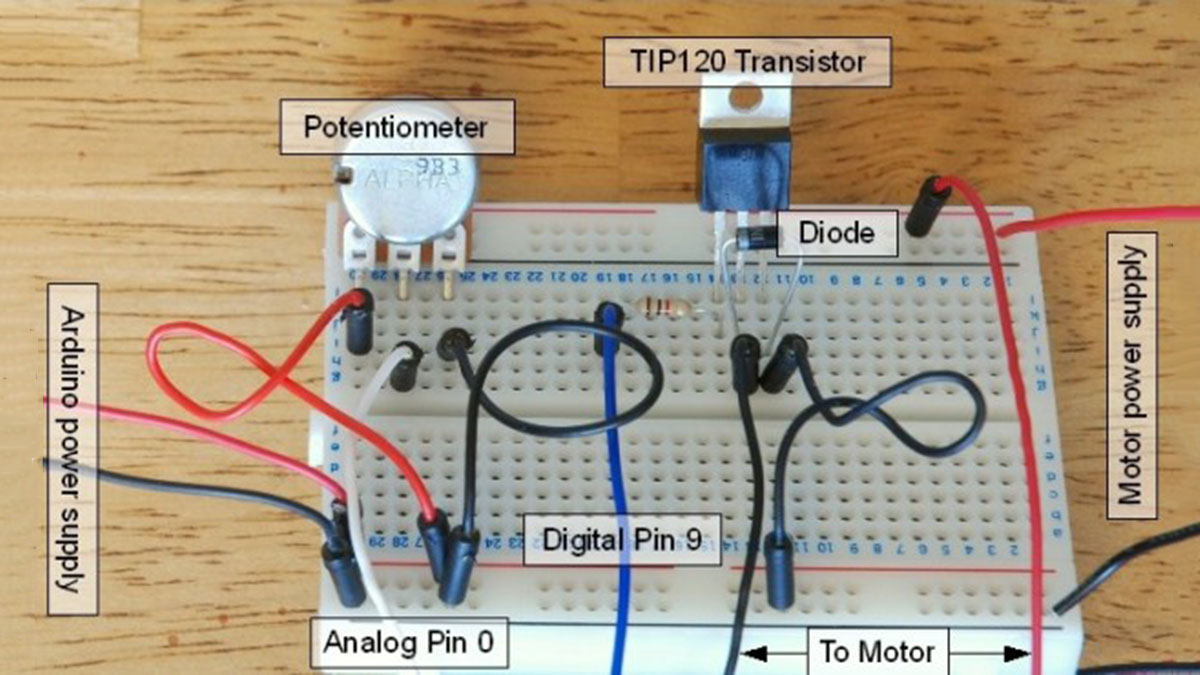
Arduino TIP120 Circuit Components
1K Ohm resistor (Brown, Black, Red, Gold)
10k Potentiometer
TIP120 Transistor
1n4004 1A Diode
6V DC motor
Arduino Deumilanove w/ ATMEGA328
Breadboard / Prototyping board
Jumper/ Connector wires
4x AA battery holder
4x AA batteries
Optional 9V DCpower supply or use the USB power for the Arduino
TIP120 Arduino DC Motor Control Circuit
Pretty simple, but remember that the GND connection must be shared between the Arduino and the additional power supply and I’m using a 1k Ohm resistor between Arduino pin 9 and the Base pin of the transistor.
TIP120 DC Motor Driver Sketch
int potPin = 0; // Analog pin 0 connected to the potentiometer
int transistorPin = 9; // connected from digital pin 9 to the base of the transistor
int potValue = 0; // value returned from the potentiometer
void setup() { // set the transistor pin as an output
pinMode(transistorPin, OUTPUT);
}
void loop() { // read the potentiometer, convert it to between 0 - 255 for the value accepted by the digital pin.
potValue = analogRead(potPin) / 4; // potValue alters the supply from pin 9 which in turn controls the power running through the transistor
analogWrite(9, potValue);
}For more detail: Arduino – Control a DC motor with TIP120, potentiometer and multiple power supplies