Summary of Arduino Button Mouse Control Code
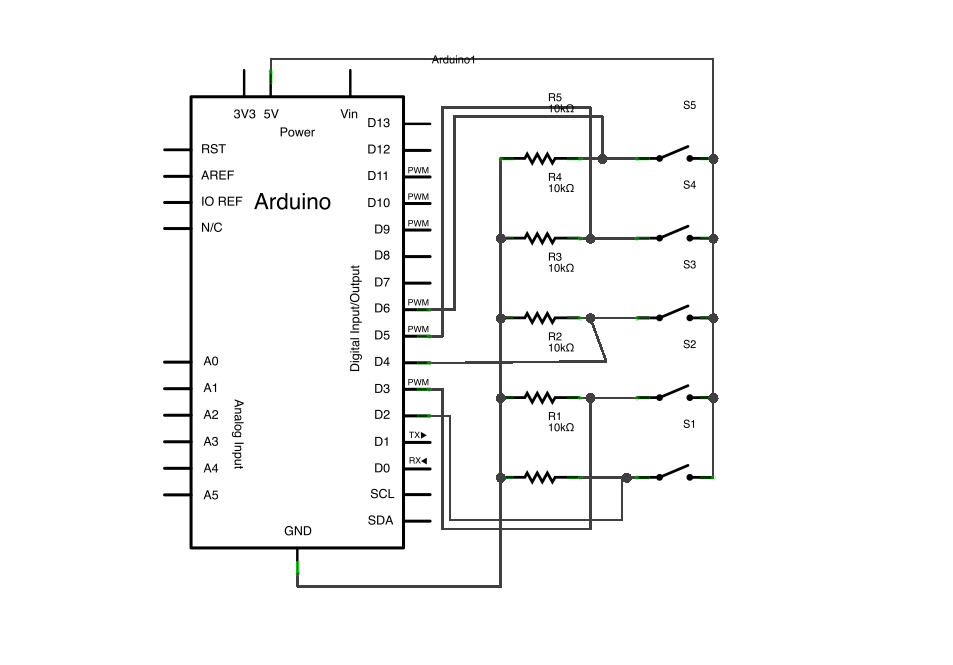
This project uses an Arduino Leonardo, Micro, or Due with the Mouse library to control a computer cursor using five pushbuttons. Four buttons move the cursor in up, down, left, and right directions by 5 units per press, while the fifth button triggers a left mouse click. The cursor movement is always relative to its current position and is updated only when buttons are pressed. Users must ensure control of their computer before using the Mouse.move() command to avoid cursor loss.
Parts used in the Arduino Button Mouse Control Project:
- Arduino Leonardo, Micro, or Due board
- 5 momentary pushbuttons
- Five 10-kilohm resistors
- Hook up wire
- Breadboard
With the Mouse library, an Arduino Leonardo, Micro, or Due can manipulate the onscreen cursor of a computer. This specific instance involves the use of five pushbuttons to control the movement of the cursor on the screen. Four buttons control direction (up, down, left, right) and one activates a left mouse click.
Cursor movement on the Arduino is consistently based on a relative position. Whenever an input is received, the cursor’s position is adjusted in relation to its existing location.
Each time a directional button is activated, the Arduino will manipulate the mouse by translating a HIGH signal into a movement of 5 units in the correct direction.
The fifth button controls a left mouse click. When the board is pressed, it sends a signal to the computer. Upon releasing the button, the computer will acknowledge the occurrence.
Note: The Arduino seizes control of your computer’s cursor when the Mouse.move() command is used! Make sure to establish a controller before using Mouse.move() to prevent losing control of your computer during the sketch. The cursor position in this sketch is only updated when a button is pressed.
Software Required
- none
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Schematic:
Code
/* ButtonMouseControl Controls the mouse from five pushbuttons on an Arduino Leonardo or Micro. Hardware: * 5 pushbuttons attached to D2, D3, D4, D5, D6 The mouse movement is always relative. This sketch reads four pushbuttons, and uses them to set the movement of the mouse. WARNING: When you use the Mouse.move() command, the Arduino takes over your mouse! Make sure you have control before you use the mouse commands. created 15 Mar 2012 modified 27 Mar 2012 by Tom Igoe this code is in the public domain */
Hardware Required
- Arduino Leonardo, Micr or Due board
- 5 momentary pushbuttons
- Five 10-kilohm resistors
- hook up wire
- breadboard
For more detail: Arduino Button Mouse Control Code