Summary of AC Power Theory – Arduino maths
The article explains how to measure and calculate AC voltage, current, and power using an Arduino or emonTx device. It describes sampling voltage and current waveforms at high frequency, calculating instantaneous power by multiplying voltage and current samples, then averaging these to find real power. It also briefly outlines computing root-mean-square (RMS) voltage by squaring samples, finding their mean, and taking the square root. The approach is relevant for monitoring power consumption in devices like laptop power supplies or incandescent bulbs.
Parts used in the Arduino AC Power Measurement Project:
- Arduino microcontroller
- Current sensor (e.g., CT - Current Transformer)
- Voltage sensor
- Sampling circuitry for voltage and current
- Power supply for Arduino and sensors
Instantaneous Voltage and current
AC Voltage and current continually alternate, as the name suggests, if we draw a picture of the voltage and current waveform over time, it will look something like the image below (depending on what’s using power – the current waveform – blue in the diagram below – is what you get if you look at a typical laptop power supply. There’s an incandescent light bulb in there as well).
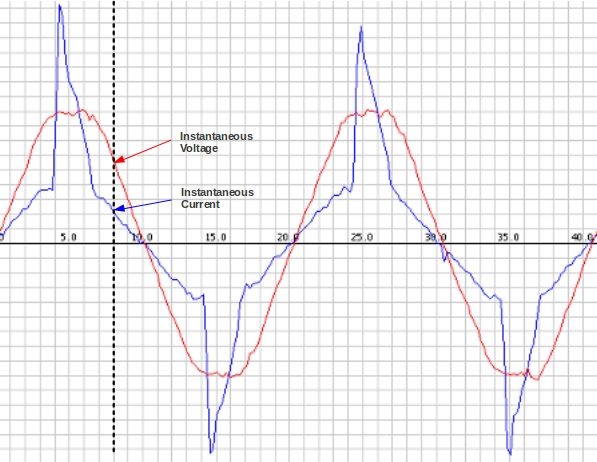 The image was made by sampling the mains voltage and current at high frequency, which is exactly what we do on the emontx or Arduino. We make between 50 and a 100 measurements every 20 milliseconds. (100 if sampling only current, and 50, if sampling voltage and current – we’re limited by the Arduino analog read command and calculation speed).
The image was made by sampling the mains voltage and current at high frequency, which is exactly what we do on the emontx or Arduino. We make between 50 and a 100 measurements every 20 milliseconds. (100 if sampling only current, and 50, if sampling voltage and current – we’re limited by the Arduino analog read command and calculation speed).
Calculating real power
Real power is the average of instantaneous power. The calculation is relatively straightforward on the Arduino.
First we calculate the instantaneous power by multiplying the instantaneous voltage measurement with the instantaneous current measurement. We sum this instantaneous power measurement over a given number of samples and divide by that number of samples:
for (n=0; n<number_of_samples; n++)
{
// inst_voltage and inst_current calculation from raw ADC input goes here
inst_power = inst_voltage * inst_current;
sum_inst_power += inst_power;
}
real_power = sum_inst_power / number_of_samples;Root-Mean-Square (RMS) Voltage
The root-mean-square is calculated in the way the name suggests first we square the quantity, then we calculate the mean and finaly the square-root of the mean-square,
For more detail: AC Power Theory – Arduino maths
