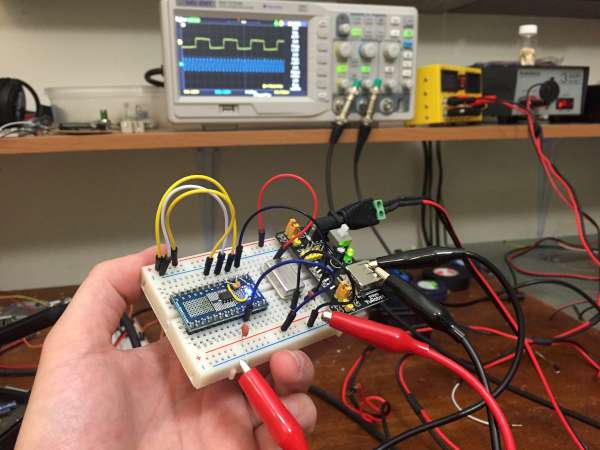
ICS501 simple frequency multiplier
Today I made a high frequency multiplier using a single component: the ICS501 PLL clock multiplier IC. This chip provides 2x, 5x, 8x (and more) clock multiplication using an internal phased-lock loop (PLL). At less than a dollar on eBay, $1.55 on mouser, and $0.67 on Digikey, they don’t break the bank and I’m glad I have a few in my […]