A group of Researchers from Purdue University in Lafayette, Indiana demonstrated the effect called negative capacitance by making a new type of more energy efficient transistor. This new kind of Field Effect Transistor (FET) proves a theory introduced in 2008 by Supriyo Datta, the Thomas Duncan Distinguished Professor of Electrical and Computer Engineering, and Sayeef Salahuddin, who is a professor of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences at the University of California, Berkeley.
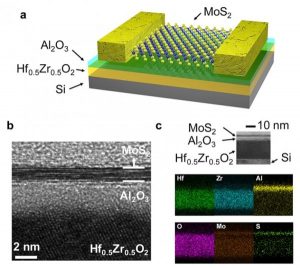
The researchers from Purdue University made a much thinner layer using the semiconductor Molybdenum disulfide. It creates a channel adjacent to an important part of transistors called the gate. By using a “ferroelectric material” called hafnium zirconium oxide, they created a negative capacitor which is a key component in the newly designed gate.
Capacitance is the property of any dielectric or conductor to store electrical charge. It is ordinarily a positive quantity. With the help of ferroelectric materials, the new FET gate structure allows a negative capacitance. Due to this the energy needed to switch the FET is considerably reduced. This new design just substitutes hafnium oxide with hafnium zirconium oxide. Hafnium oxide is a conventional material to use in modern FETs as a dielectric material to isolate the gate. This work is led by Peide Ye, Richard J. and Mary Jo Schwartz of Purdue University. Ye said,
The overarching goal is to make more efficient transistors that consume less power, especially for power-constrained applications such as mobile phones, distributed sensors, and emerging components for the internet of things
Read more: Researchers Demonstrate New More Efficient FET By Implementing Negative Capacitance