Introduction
Microcontrollers like the Arduino were designed to facilitate the use of electronics for designers and DIY enthusiasts. The interface provides a great starting points for a variety of elecronic circuit designs. However, as the microcontroller is standardized, it is also limited in its use. That shows for example in the limited number of PWM (pulse width modulation) enabled output pins.
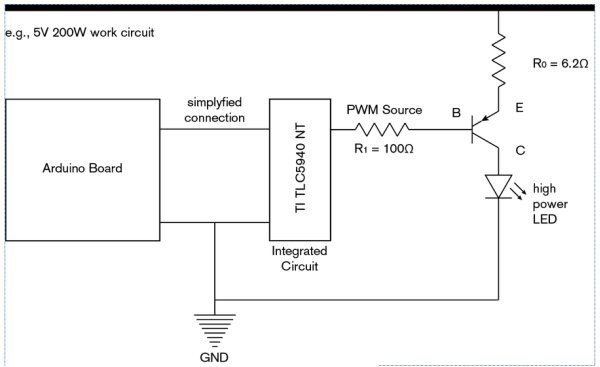
 What can you do to extend the PWM capabilities of your Arduino? Just buy a bigger one? That is not necessary anymore after you have read this article. Here it is shown how to connect an Arduino microcontroller to a Texas Instruments TLC5940 LED Driver to connect a large number of LEDs, or even power-intensive devices such as star-mounted high power RGB LEDs or servo motors.
What can you do to extend the PWM capabilities of your Arduino? Just buy a bigger one? That is not necessary anymore after you have read this article. Here it is shown how to connect an Arduino microcontroller to a Texas Instruments TLC5940 LED Driver to connect a large number of LEDs, or even power-intensive devices such as star-mounted high power RGB LEDs or servo motors.
In the design of digital musical instruments (DMIs), this is particularily useful to provide different kinds of feedback to the performer while maintining high extensibility at a lower cost.
Capabilities
The datasheet of the TLC5940 is available from Texas Instruments, amongst other useful information such as application notes and the option to request samples.
A selection of important features:
| Number of channels | 16 |
| Resolution | 12 bit (4096 steps) |
| Drive Capability | 0 mA to 120 mA (for VCC > 3.6 V) |
Connectable actuators
Many electrical components can be controlled using a PWM signal. Not only LEDs can be dimmed, but also Servo motors can be driven, as well as DC motors.
Daisy chaining
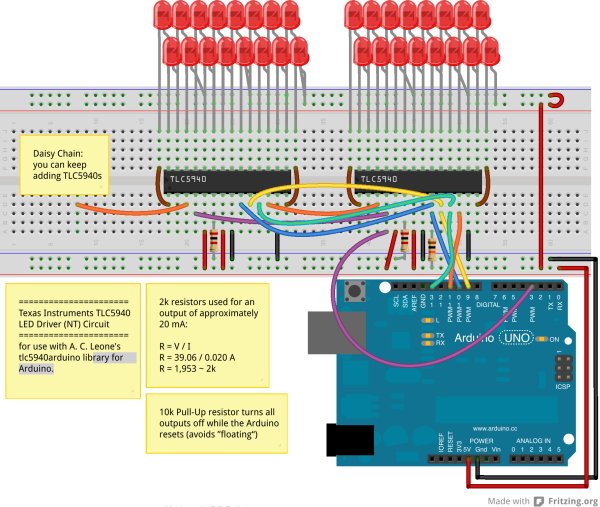
Daisy chaining means that you can wire multplie devices together in series. In our case, we can not only extend the PWM pins with one TLC5940 with 16 pins, but because of the daisy-chain ability even use multiple TLC5940s to output 32, 48 or 64 PWM signals.
For more detail: Extending PWM output pins with a Texas Instruments TLC5940 LED driver