Summary of Arduino LED Bar Graph Code
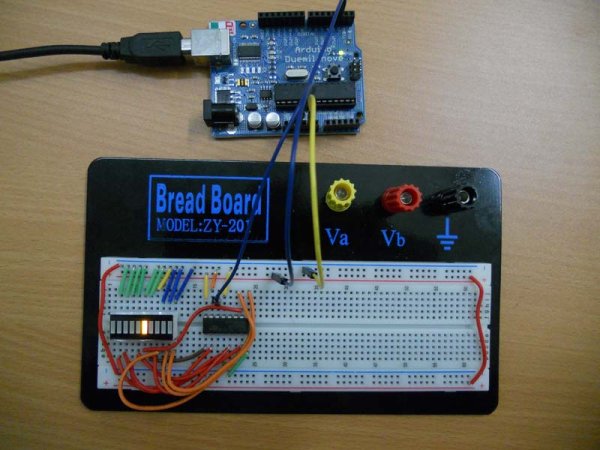
This tutorial explains how to create an LED bar graph display controlled by an analog sensor input using an Arduino. It involves reading an analog input, mapping it to the number of LEDs to light up (typically 10), and using a for loop to turn LEDs on or off accordingly. The circuit connects LEDs (or an LED bar graph) to Arduino digital pins 2 through 11 with appropriate resistors. This setup can be adapted for controlling any digital outputs based on an analog input.
Parts used in the LED Bar Graph Project:
- Arduino Board
- LED bar graph display or 10 individual LEDs
- 220 ohm resistors (10 pieces)
- Hook-up wire
- Breadboard
The bar graph – a series of LEDs in a line, such as you see on an audio display – is a common hardware display for analog sensors.
It’s made up of a series of LEDs in a row, an analog input like a potentiometer, and a little code in between. You can buy multi-LED bar graph displays fairly cheaply, like this one. This tutorial demonstrates how to control a series of LEDs in a row, but can be applied to any series of digital outputs.
This tutorial borrows from the For Loop and Arrays tutorial as well as the Analog Input tutorial.
The sketch works like this: first you read the input. You map the input value to the output range, in this case ten LEDs. Then you set up a for loop to iterate over the outputs. If the output’s number in the series is lower than the mapped input range, you turn it on. If not, you turn it off.
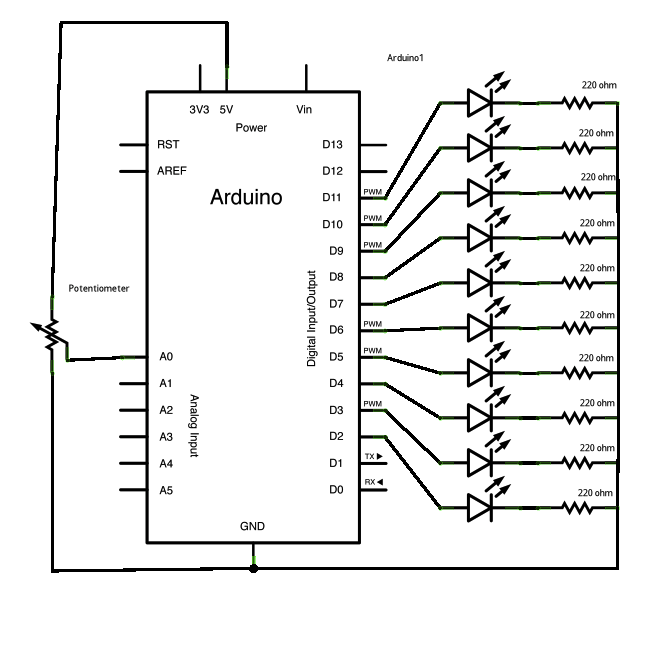
Circuit
Image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Schematic:
Code
/* LED bar graph Turns on a series of LEDs based on the value of an analog sensor. This is a simple way to make a bar graph display. Though this graph uses 10 LEDs, you can use any number by changing the LED count and the pins in the array. This method can be used to control any series of digital outputs that depends on an analog input. The circuit: * LEDs from pins 2 through 11 to ground created 4 Sep 2010 by Tom Igoe This example code is in the public domain. http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/BarGraph */
Hardware Required
- Arduino Board
- (1) LED bar graph display or 10 LEDs
- (10) 220 ohm resistors
- hook-up wire
- breadboard
For more detail: Arduino LED Bar Graph Code