This demonstrates how to use your Arduino MKR1000 to connect to InitialState.com to produce colorful visualizations of your sensor data.
Things used in this project
Story
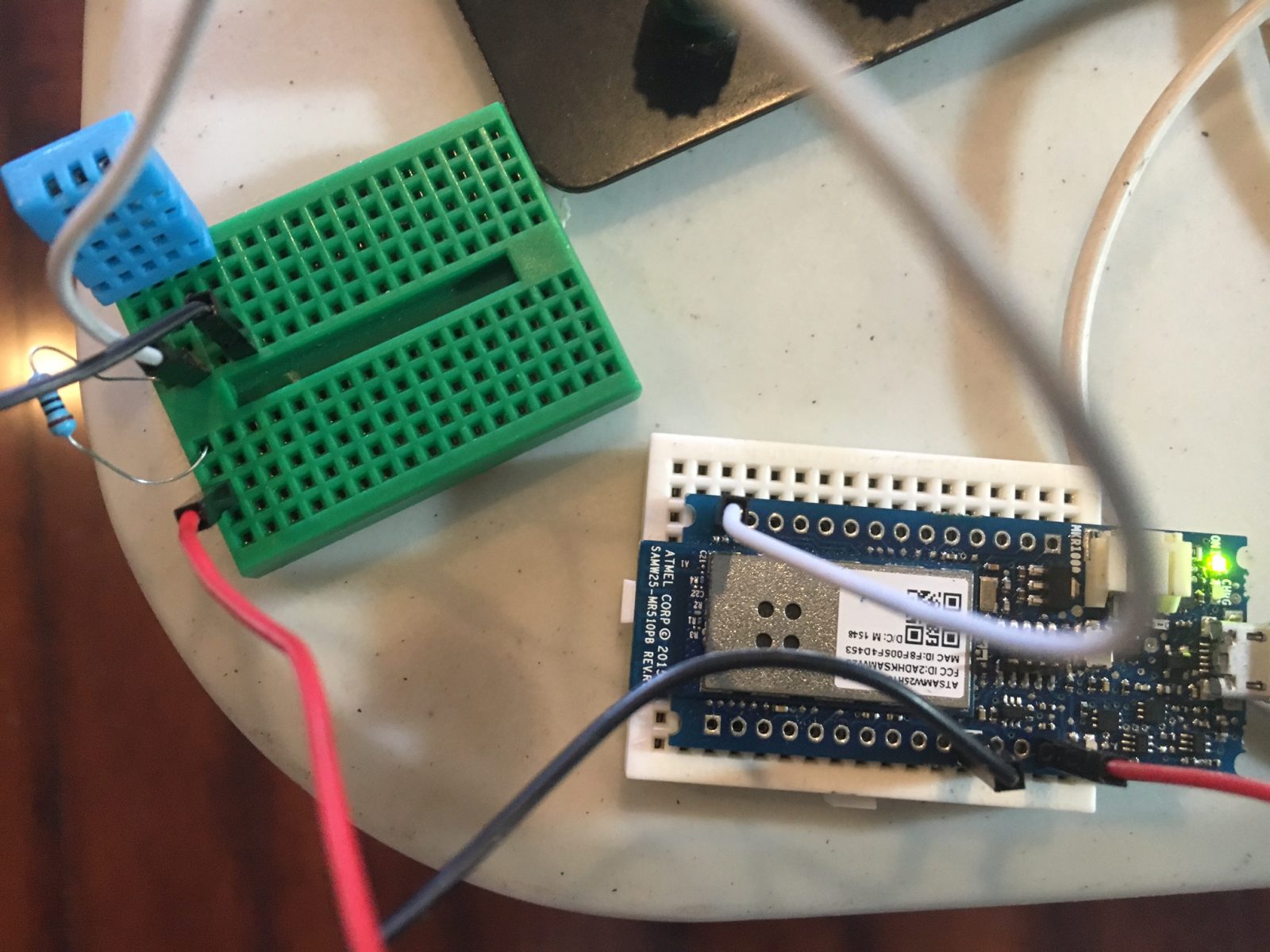
This tutorial will explain how to upload sensor data from the ubiquitous DHT sensor, attached to the Arduino MKR1000 WiFi device, to the Initial State website. Initial State is a website similar to ThingSpeak.com (see my other tutorial on Hackster.io). InitialState.com has both paid and free tier accounts available. I will be using the free tier in this demonstration to show how to get graphs, charts and numeric data logging all from the Initial State website. Like most similar free cloud IoT data sites for makers and hacksters, the code we use is very similar between these websites. Where we see the fundamental difference is in how the RESTful API string is constructed, concatenated, and formatted to allow the communication between the embedded device and IoT website to concur successfully. These websites tend to be very strict on how to properly construct the API REST strings to function successfully.
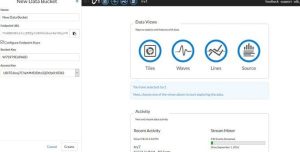
Our first step in this process is to register for a free account on InitialState.com and create a new visualization. You can create the visualization but clicking the cloud icon. You should name your visualization anything you like.
After creating our new visualization we will need to copy our API key(called Access key here) and Bucket Key. Both these are provided by alphanumeric digits. We can rename our Bucket Key to anything with like, however each visualization needs a unique Bucket Key name. You will only have one API key throughout all your visualizations, this is used to identify your account not your specific visualization (that’s what the bucket key is used for). If you forget your Access/API key you can generate a new one at any time linked to your account.
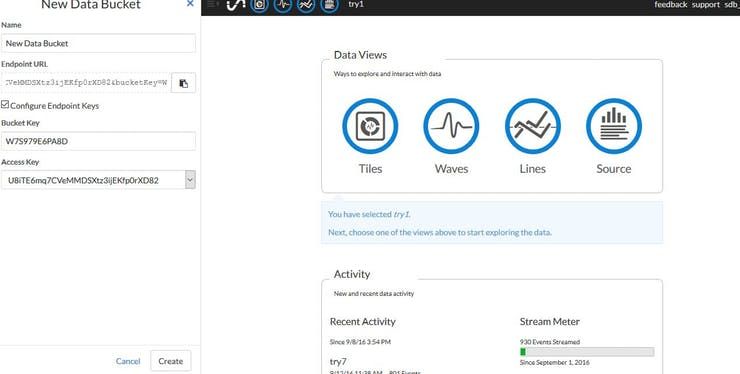
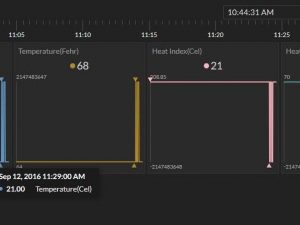
From this point we can now add new tiles with custom parameters to our visualizations. We also have default line charts and wave charts available for every visualizations as well as a simple data logger for raw numbers which can be downloaded to your computer. Overall it is an impressive free package for data logging over the cloud. On the free tier your data is only saved for 24 hours.
Now that we established our free account, and customized our graphs and charts to output visualizations how we like, we can use our MKR1000 to upload data to our account.
Remember to save your Bucket Key (Default or renamed) and Access Key to use in the Arduino MKR1000 sketch. Once you have successfully connected to Initial State in the cloud you will see your graphs, charts, and other visualizations getting updated with your uploaded sensor data.
I will try to do the same tutorial for the Intel Edison and ESP8266. My code is based upon a modified example for the Ethernet Shield example provided by Initial State, RChloe and Gaetano Carlucci. I also added section to use DHT output and WiFi info but it is easy to alter for most any sensor.
Schematics
Code