Using Intel Edison as gateway and redirecting data from Arduimo MKR1000 to Microsoft Azure IoTHub.
Things used in this project
Story
Background
Workshop project during Intel Edison/Microsoft Azure meetup.
Prerequisites
To make this project please prepare :
- Microsoft Azure IoT Hub (link)
- Arduino web editor account (link)
Description
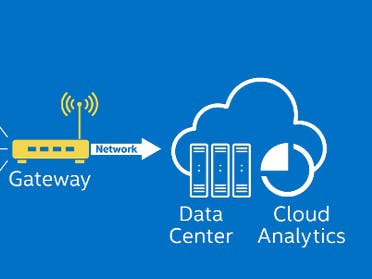
Arduino MKR1000 send JSON message with data to Intel Edison using UDP protocol. On receving event Intel Edison resend message to Azure IoTHub. For developing Arduino MKR1000 sketch we were using new Arduino web editor! NodeJS app for Intel edison has been developed by Microsoft Visual Studio Code.
Screenshots
Code
Arduino.ino
Arduino
#include <ArduinoJson.h>
#include <SPI.h>
#include <WiFi101.h>
#include <WiFiUdp.h>
#include <DHT.h>
int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS;
char ssid[] = "TP-LINK"; // your network SSID (name)
char pass[] = "Samba2015"; // your network password (use for WPA, or use as key for WEP)
char buf[200];
unsigned int localPort = 3030; // local port to listen on
IPAddress edisonServer(10,10,0,82);
char ReplyBuffer2[] = "acknowledged"; // a string to send back
WiFiUDP Udp;
#define DHTPIN 2
#define DHTTYPE DHT11
DHT dht(DHTPIN, DHTTYPE);
void setup() {
//Initialize serial and wait for port to open:
Serial.begin(9600);
//while (!Serial) {
//; // wait for serial port to connect. Needed for native USB port only
//}
dht.begin();
// check for the presence of the shield:
if (WiFi.status() == WL_NO_SHIELD) {
Serial.println("WiFi shield not present");
// don't continue:
while (true);
}
// attempt to connect to Wifi network:
while ( status != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to SSID: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
// Connect to WPA/WPA2 network. Change this line if using open or WEP network:
status = WiFi.begin(ssid,pass);
// wait 10 seconds for connection:
delay(10000);
}
Serial.println("Connected to wifi");
printWifiStatus();
Serial.println("\nStarting connection to server...");
// if you get a connection, report back via serial:
Udp.begin(localPort);
}
void loop() {
float h = dht.readHumidity();
// Read temperature as Celsius (the default)
float t = dht.readTemperature();
StaticJsonBuffer<200> jsonBuffer; // reserve spot in memory
JsonObject& root = jsonBuffer.createObject(); // create root objects
root["sdid"] = "<YOUR DEVICE ID>"; // FIX
root["type"] = "message";
JsonObject& dataPair = root.createNestedObject("data"); // create nested objects
dataPair["temp"] = t;
dataPair["humid"] = h;
root.printTo(buf, sizeof(buf)); // JSON-print to buffer
// send a reply, to the IP address and port that sent us the packet we received
Udp.beginPacket(edisonServer, 41235);
Udp.write(buf);
Udp.endPacket();
delay(1*60*1000);
}
void printWifiStatus() {
// print the SSID of the network you're attached to:
Serial.print("SSID: ");
Serial.println(WiFi.SSID());
// print your WiFi shield's IP address:
IPAddress ip = WiFi.localIP();
Serial.print("IP Address: ");
Serial.println(ip);
// print the received signal strength:
long rssi = WiFi.RSSI();
Serial.print("signal strength (RSSI):");
Serial.print(rssi);
Serial.println(" dBm");
}Source : Intel Edison as Azure IoTHub gateway




