This example demonstrates multi-byte communication from the Arduino board to the computer using a call-and-response (handshaking) method.
This sketch sends an ASCII A (byte of value 65) on startup and repeats that until it gets a serial response from the computer. Then it sends three sensor values as single bytes, and waits for another response from the computer.
You can use the Arduino serial monitor to view the sent data, or it can be read by Processing (see code below), Flash, PD, Max/MSP (see example below), etc.
Software Required
Circuit
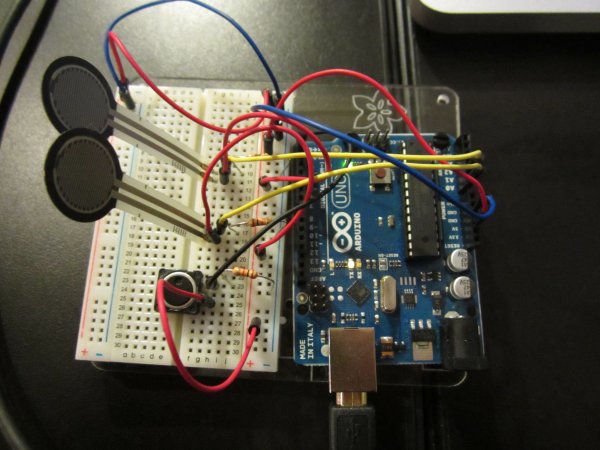
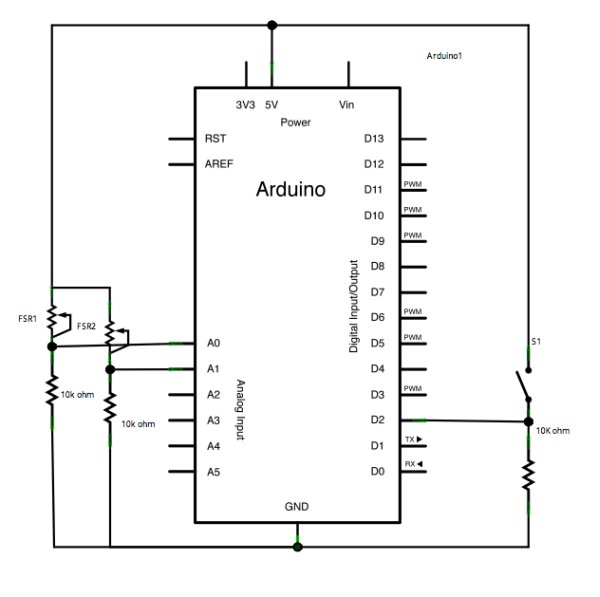
Connect analog sensors to analog input pin 0 and 1 with 10K ohm resistors used as voltage dividers. Connect a pushbutton or switch to digital I/O pin 2 with a 10Kohm resistor as a reference to ground.
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Schematic
Code
Serial Call and Response
Language: Wiring/Arduino
This program sends an ASCII A (byte of value 65) on startup
and repeats that until it gets some data in.
Then it waits for a byte in the serial port, and
sends three sensor values whenever it gets a byte in.
Thanks to Greg Shakar and Scott Fitzgerald for the improvements
The circuit:
* potentiometers attached to analog inputs 0 and 1
* pushbutton attached to digital I/O 2
Created 26 Sept. 2005
by Tom Igoe
modified 24 April 2012
by Tom Igoe and Scott Fitzgerald
This example code is in the public domain.
http://www.arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/SerialCallResponse
*/
int firstSensor = 0; // first analog sensor
int secondSensor = 0; // second analog sensor
int thirdSensor = 0; // digital sensor
int inByte = 0; // incoming serial byte
void setup()
Hardware Required
- Arduino Board
- (2) analog sensors (potentiometer, photocell, FSR, etc.)
- (1) momentary switch/button
- (3) 10K ohm resistors
- breadboard
- hook-up wire