This example shows how to use the tone() command to generate a pitch that follows the values of an analog input

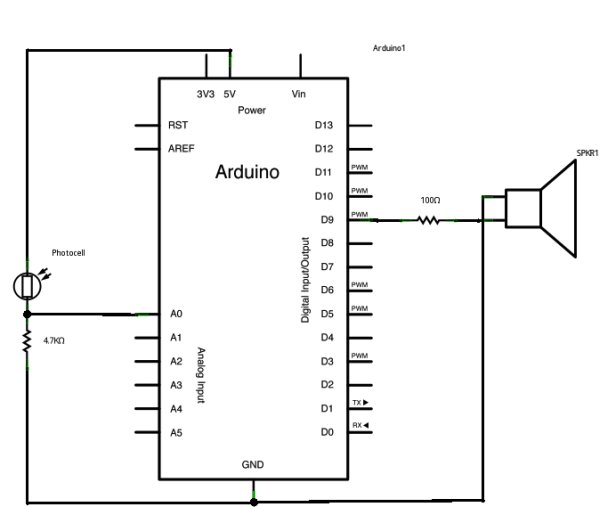
Circuit
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Connect one terminal of your speaker to digital pin 9 through a 100 ohm resistor, and its other terminal to ground. Power your photoresistor with 5V, and connect it to analog 0 with the addition of a 4.7K resistor to ground.
Schematic
Code
The code for this example is very simple. Just take an analog input and map its values to a range of audible pitches. Humans can hear from 20 – 20,000Hz, but 120 – 1500 usually works pretty well for this sketch.
You’ll need to get the actual range of your analog input for the mapping. In the circuit shown, the analog input value ranged from about 400 to about 1000. Change the values in the map() command to match the range for your sensor.
The sketch is as follows:
Pitch follower
Plays a pitch that changes based on a changing analog input
circuit:
* 8-ohm speaker on digital pin 8
* photoresistor on analog 0 to 5V
* 4.7K resistor on analog 0 to ground
created 21 Jan 2010
modified 31 May 2012
by Tom Igoe, with suggestion from Michael Flynn
This example code is in the public domain.
http://arduino.cc/en/Tutorial/Tone2
*/
Hardware Required
- 8-ohm speaker
- 1 photocell
- 4.7K ohm resistor
- 100 ohm resistor
- breadboard
- hook up wire