Researchers at Stanford University have demonstrated the acceleration of electrons through what they describe as an “On-chip integrated laser-driven particle accelerator”, detailed in a recent paper published in the Science journal. by Tom Abate
On a hillside above Stanford University, the SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory operates a scientific instrument nearly 2 miles long. In this giant accelerator, a stream of electrons flows through a vacuum pipe, as bursts of microwave radiation nudge the particles ever-faster forward until their velocity approaches the speed of light, creating a powerful beam that scientists from around the world use to probe the atomic and molecular structures of inorganic and biological materials.
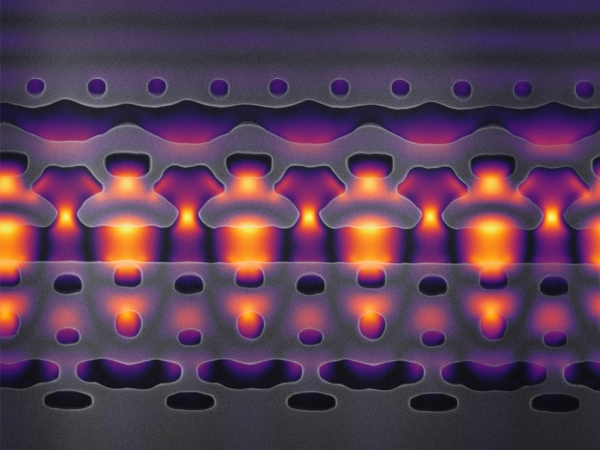
This image, magnified 25,000 times, shows a section of an accelerator-on-a-chip. The gray structures focus infrared laser light (shown in yellow and purple) on electrons flowing through the center channel. By packing 1,000 channels onto an inch-sized chip, Stanford researchers hope to accelerate electrons to 94 percent of the speed of light. (Image credit: Courtesy Neil Sapra)
Now, for the first time, scientists at Stanford and SLAC have created a silicon chip that can accelerate electrons – albeit at a fraction of the velocity of that massive instrument – using an infrared laser to deliver, in less than a hair’s width, the sort of energy boost that takes microwaves many feet.
Writing in the Jan. 3 issue of Science, a team led by electrical engineer Jelena Vuckovic explained how they carved a nanoscale channel out of silicon, sealed it in a vacuum and sent electrons through this cavity while pulses of infrared light – to which silicon is as transparent as glass is to visible light – were transmitted by the channel walls to speed the electrons along.
The accelerator-on-a-chip demonstrated in Science is just a prototype, but Vuckovic said its design and fabrication techniques can be scaled up to deliver particle beams accelerated enough to perform cutting-edge experiments in chemistry, materials science and biological discovery that don’t require the power of a massive accelerator.
“The largest accelerators are like powerful telescopes. There are only a few in the world and scientists must come to places like SLAC to use them,” Vuckovic said. “We want to miniaturize accelerator technology in a way that makes it a more accessible research tool.”
Read more: PARTICLE ACCELERATOR FITS ON A CHIP
