Sometimes you need to do two things at once. For example you might want to blink an LED (or some other time-sensitive function) while reading a button press or other input. In this case, you can’t use delay(), or you’d stop everything else the program while the LED blinked. The program might miss the button press if it happens during the delay(). This sketch demonstrates how to blink the LED without using delay(). It keeps track of the last time the Arduino turned the LED on or off. Then, each time through loop(), it checks if a long enough interval has passed. If it has, it toggles the LED on or off.
Circuit
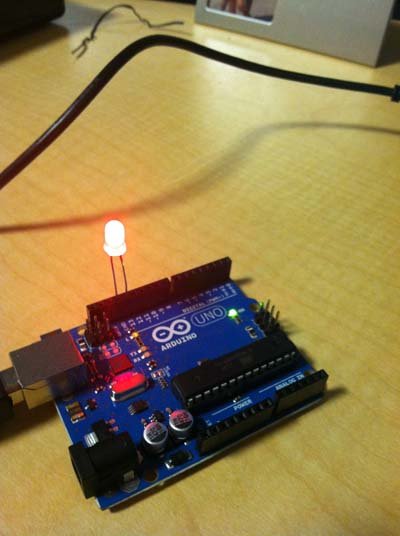
To build the circuit, grab an LED and attach its long, positive leg (called the anode) to pin 13. Attach the short, negative leg (called the cathode) to ground. Then plug your Arduino board into your computer, start the Arduino program, and enter the code below.
Schematic:
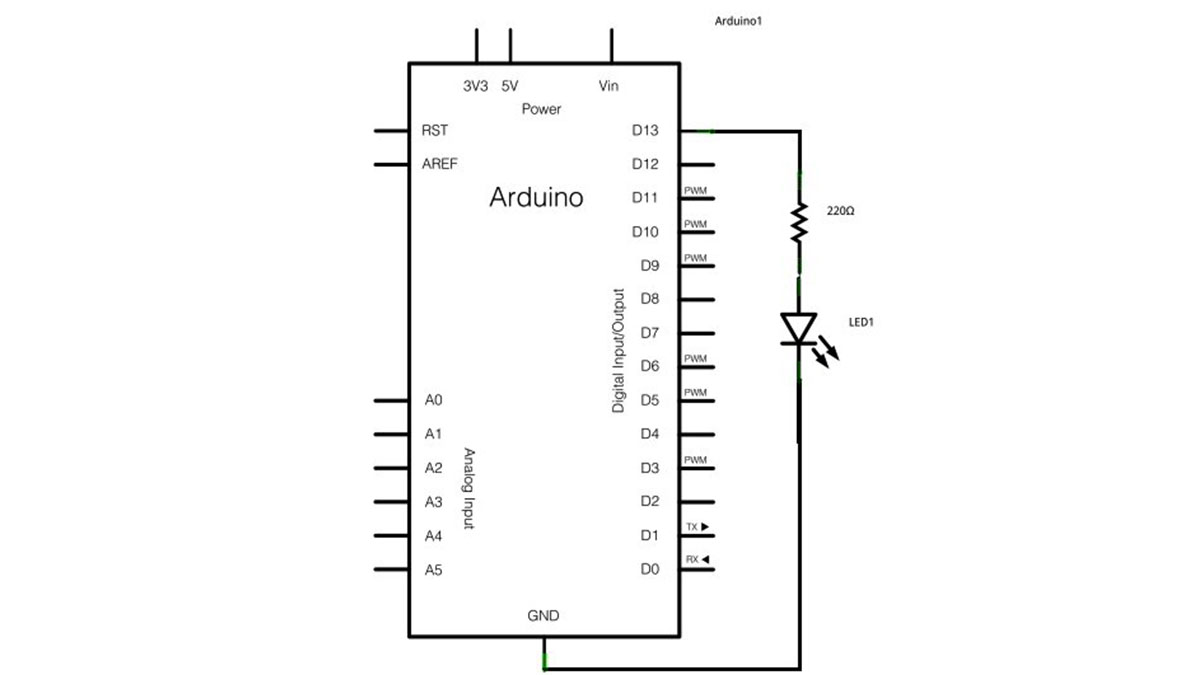
image developed using Fritzing. For more circuit examples, see the Fritzing project page
Code
The code below uses the millis() function, a command that returns the number of milliseconds since the Arduino board started running its current program, to blink an LED.
Turns on and off a light emitting diode(LED) connected to a digital
pin, without using the delay() function. This means that other code
can run at the same time without being interrupted by the LED code.
The circuit:
* LED attached from pin 13 to ground.
* Note: on most Arduinos, there is already an LED on the board
that’s attached to pin 13, so no hardware is needed for this example.
Hardware Required
- Arduino Board
- LED

