By coupling a standard NMEA GPS receiver and an Arduino board we created a super simple and effective Arduino GPS logger. This device allows you to trace the route taken by a person or vehicle (or any other moving object) by simply doing a periodic caching of location points coming from the GPS unit. As the logger saves the list of records (containing data on recorded positions) on a microSD memory card, you can then move the data onto your computer and keep track of your trip. You can use tracked data to help project such as OpenStreetMap to grow and include new areas (www.openstreetmap.org)
An intelligent logger
Being experienced users of other loggers in the market, we realized that one of the most annoying things is to forget to turn it off once you get to destination. This means consuming memory because the device continuously saves almost the same position. For this reason we decided to implement a system that is able to stop recording when the logger is still. This feature was obtained thanks to an accelerometer which, in addition to stop saving data when the tracker has stopped, also allows to turn off the GPS module to reduce consumption, which is useful, since this kind of systems normally feeds on batteries.
Hardware
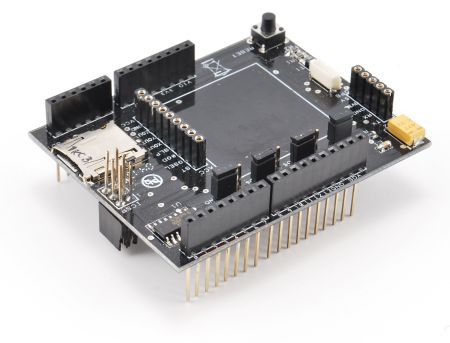
As said, the logger consists of a shield, on which there are mainly the GPS receiver, the SD-Card reader and the accelerometer, in addition to an Arduino UNO board. The GPS receiver is connected through two connectors (each one alternative to the other) then you can actually place it out of the shield. This can be useful if you plan to mount more shields above the circuit, which inevitably disturb the reception of satellites signals.
Let’s look at the circuit of the shield, which, by virtue of its reduced power consumption, it is powered directly from the Arduino. Our measures, when powering it with the Arduino 5V, indicate a consumption of around 35 mA, with the GPS on, reduced to about 5 mA by turning it off via pin 7.
Moreover, we have the 40 mA of the Arduino ONE, for a total of 75 mA in LOG mode (ie during the acquisition and recording of coordinates) and 45 mA in standby mode.
For more detail: An Arduino powered, easily extendable GPS Datalogger