Abstract: This design idea presents an integrated IF voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) that can retransmit the audio signal from a cell phone to the FM broadcast band. By placing the cell phone’s speaker near the microphone, the user can use the phone as a hands-free device while driving.

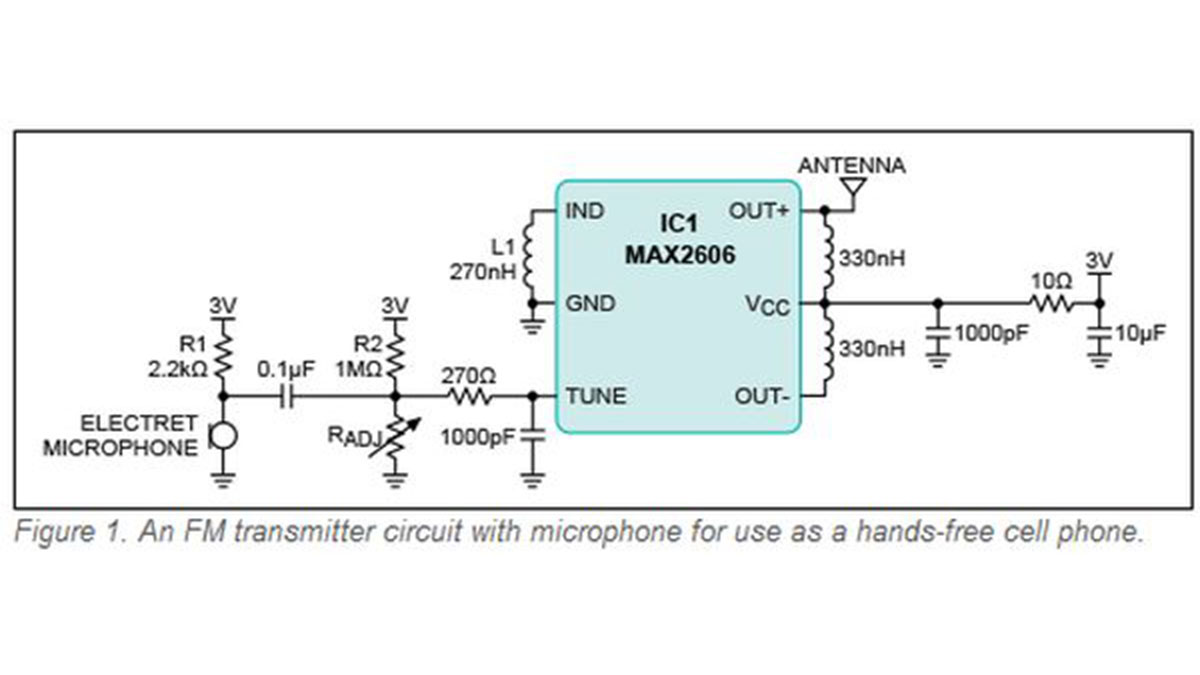
The circuit in Figure 1 can retransmit the audio signal from a cell phone to the FM broadcast band. When the user places a cell phone speaker near the microphone, he or she can listen to the cell phone audio via the vehicle’s FM radio. This can be used as an in-car hands-free speakerphone.
IC1 is an integrated IF
voltage-controlled oscillator (VCO) with a
differential output that supports a 70MHz to 150MHz frequency range, which covers the whole FM radio band. Inductor L1 sets the VCO’s center tuning range. Select L1 such that the effective inductance from the IND pin to GND results in an output frequency of 100MHz.This frequency corresponds with the center of the FM band. An inductor value of 270nH covers a tuning 97MHz to 128MHz range. Next, adjust the R
ADJ resistor to tune the VCO to a particular FM station frequency. Resistors R2 and R
ADJ bias the internal varactor. FM stations are located on odd 0.2MHz intervals. The VCO is capable of a differential output power of up to -8dBm. Refer to the FCC’s Title 47 CFR Part 15 for current emission regulations. Transmissions must be below 250µV, measured at 3m.
The electret microphone is biased with R1. The AC-coupled microphone audio signal modulates the VCO frequency by changing V
TUNE. The output frequency of the VCO will follow the volume or amplitude from the microphone. An audio signal with approximately 20mV
RMS is adequate for functionality. Do not over-modulate the VCO, or the resulting audio from the FM
receiver will be distorted. Over-modulating the VCO also weakens the carrier signal by emitting power onto the unused spectrum by the receiver. In
Figure 2, the microphone and R1 are replaced with a direct connection to the audio output port of a cell phone. The cell phone’s volume needs to be adjusted accordingly for optimal performance. A direct connection to the cell phone will eliminate background noise from the microphone.