ow my Arduino can precisely measure audio input (VU meter), and obviously, next thing that comes to mind right after measurements, is regulation or control. There are many different ways how to electronically adjust audio volume or level of AC signal. I’ll name a few:
- Specifically design IC, Digital potentiometers.
- Mechanical potentiometers, driven by servo / motors.
- Vacuum tubes amplifiers in “variable-mu” configuration.
- Resistive opto-isolators.
First category (#1) fits nicely for arduino project. But it’s not interesting to me. My apologies to someone, who was searching an example of interface between arduino and digital pot. Other people don’t tolerate semiconductors in audio path ( tube sound lovers ). Third option would make them happy, only (#3) requires high voltage and difficult to accomplish on low hobbyist budget, so I left it out of the scope. Mechanical pot (#2) would be good solution to satisfy Hi-Fi perfectionists and arduino fans. The same time response time of mechanical parts is too slow, verdict – discarded. (#4) have been in use since 1960s, but would you like your lovely music to be adjusted by highly toxic CdSe / CdS ? I don’t think so. Wiki says opto-isolators have low THD distortion level, less than 0.1%. Probably true, but apart from technical aspect, there is always psychological, poisonous CdSe affects my perception.
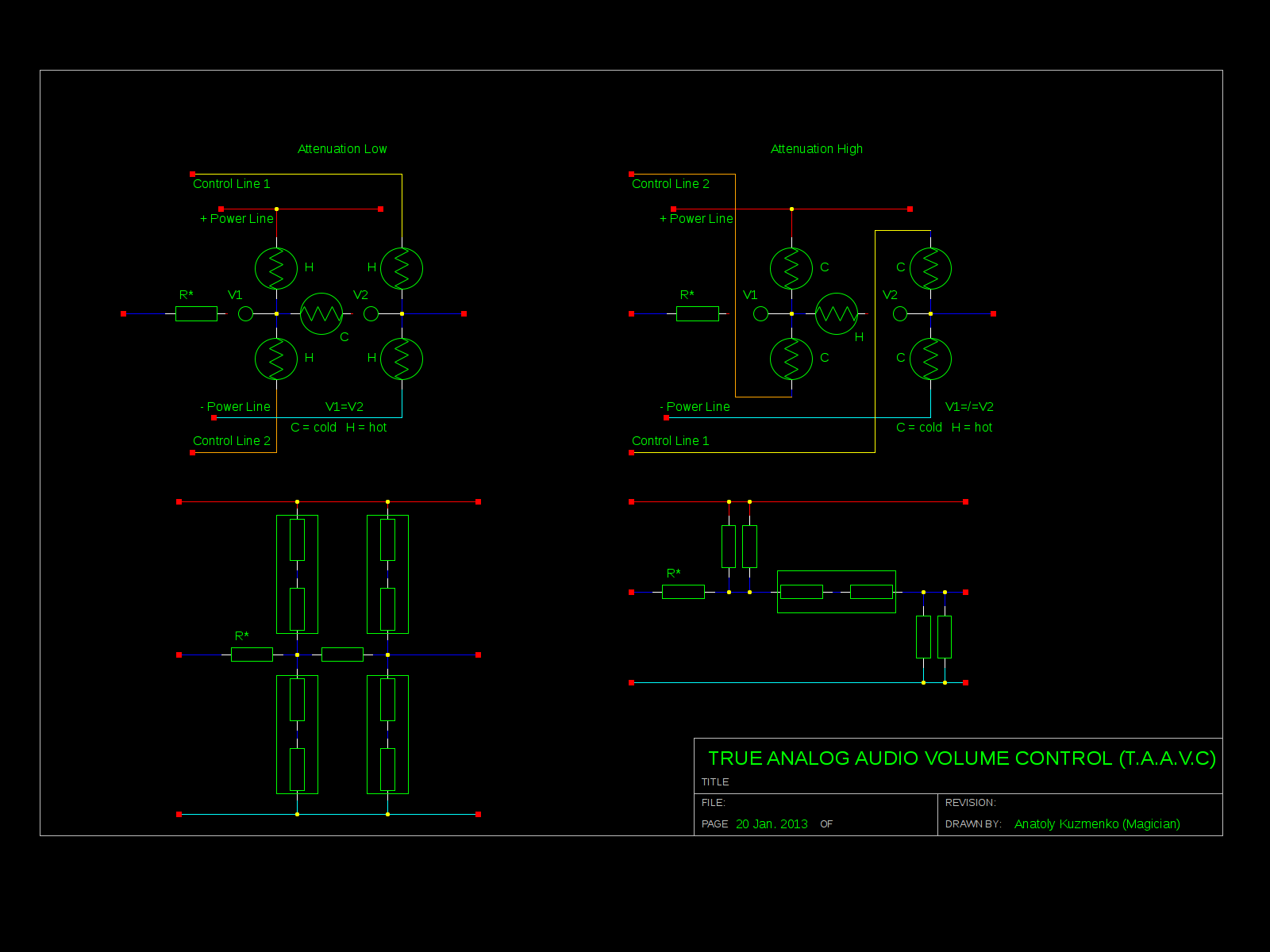
How about variable resistor in it’s simplest form – tungsten wire? Where you can get one? In the electrical bulb. Perfect material for audiophiles – where distortion could get into ? – It’s pure metal ! And here is my design of the “basic cell” – True Analog Audio Volume Control (T.A.A.V.C.)
As you can see, cell consists of 5 bulbs plus 1 resistor. All elements form 2 attenuation stages, basically – voltage dividers with variable resistors. Resistive values of bulbs proportional to temperature, which is easy to control passing DC current through. To make it work with the biggest possible dynamic range, middle bulb is also heated up by current flow from two differential control lines / phases.
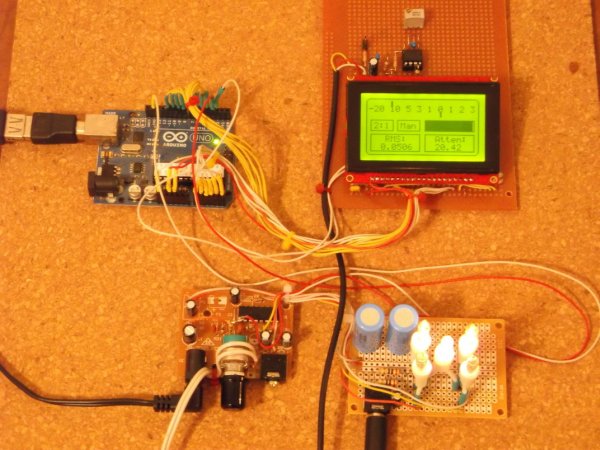
Hardware prototype / Proof of Concept.
Differential Power Amplifier (PA) IC LM4863 is used as DC current source for control lines. Circuitry powered from 5V regulated switching power supply (4A). Bulbs – clear mini lights, 2.5V, approximately 200 mA. Cold state resistance about 1.2 – 1.5 Ohm, hot state resistance is rising up to 15 Ohm. Volume regulator could be connected to any audio source with output impedance no more than 32 Ohm, for example, headphones output. For test I used second channel of the PA, that shown in “optional” box on the left side. Second channel is a “nice to have” feature in stereo version of the project, when both channels would drive two separate TAAVC cells, so using it as a “buffer” amplifier may be not an option.
[box color=”#985D00″ bg=”#FFF8CB” font=”verdana” fontsize=”14 ” radius=”20 ” border=”#985D12″ float=”right” head=”Major Components in Project” headbg=”#FFEB70″ headcolor=”#985D00″]Arduino[/box]
For more detail: True Analog Audio Volume Control using Arduino