Learn how to connect a simple web app written in JavaScript to Arduino Cloud.
Things used in this project
Story
Following this tutorial you are going to learn how to make your Arduino or Genuino MKR1000 or WiFi Shield 101 interact with a simple webpage hosted in a browser via Arduino Cloud.
Connect to Arduino Cloud
If this is the first time you are using Arduino Cloud we highly encourage to follow the getting started guide.
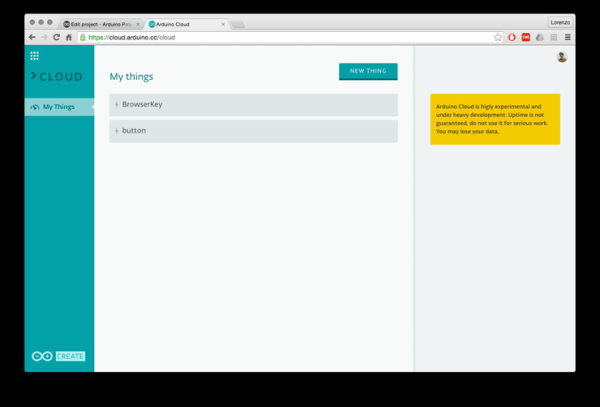
Start by creating a new thing, we are going to call this thing “button”!

Once created, take note of the credentials, you will need to insert those in the Arduino Sketch.
Now you have to create a second set of credentials that are going to be used by the browser to connect to Arduino Cloud.
The Arduino Sketch
If you followed the Arduino Cloud getting started flow, you can start coding the Arduino sketch using the one you downloaded as a starting point.
Otherwise just copy-paste the one down here and start filling in the data required to connect to your wifi and your device credential.
#include <SPI.h>
#include <WiFi101.h>
#include <WiFiSSLClient.h>
#include <MQTTClient.h>
const char ssid[] = "***";
const char pass[] = "***";
const char server[] = "mqtt.arduino.cc";
const char userName[] = "***";
const char deviceName[] = "button";
const char deviceId[] = "**************************";
const char devicePsw[] = "**************************";
MQTTClient client;
WiFiSSLClient net;
int ledPin = LED_BUILTIN;
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
pinMode(ledPin, OUTPUT);
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to WPA SSID: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
// Connect to WPA/WPA2 network:
while (WiFi.begin(ssid, pass) != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("failed ... ");
delay(4000);
Serial.print("retrying ... ");
}
client.begin(server, 8883, net);
connect();;
}
void connect() {
Serial.println("connecting...");
while (!client.connect(deviceName, deviceId, devicePsw)) {
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("connected!");
}
void loop() {
client.loop();
client.publish("/<username>/<devicename>/blink", "on");
Serial.println("publishing up");
digitalWrite(ledPin, HIGH);
delay(1000);
client.publish("/<username>/<devicename>/blink", "off");
Serial.println("publishing low");
digitalWrite(ledPin, LOW);
delay(1000);
}
void messageReceived(String topic, String payload, char * bytes, unsigned int length) {
Serial.print("incoming: ");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print(" - ");
Serial.print(payload);
Serial.println();
}
In this example sketch we are using the function client.publish() to send messages to the Arduino Cloud. To be more specific, we are sending MQTT messages to the topic at this address:
/<username>/<devicename>/blink
Devices can send value to a topic while other devices can subscribe to that same topic and listen to it.
Because of how Arduino Cloud is configured, each thing can just publish messages to a topic after /<username>/<devicename>/ . Therefore two devices cannot publish to the same topic.
Every device, however, can subscribe to all the topic after /<username>/ , thus allowing each device to listen to all the messages coming from devices under the same user account.
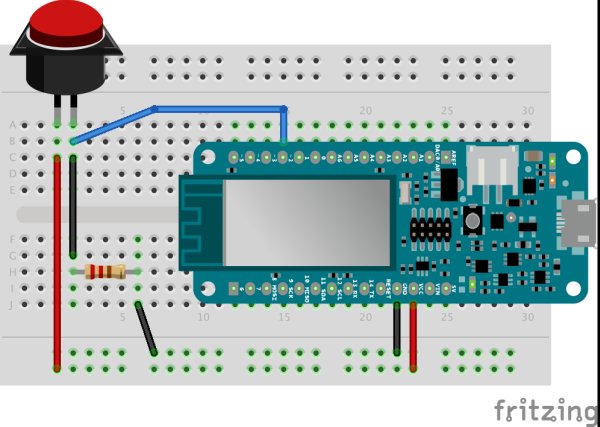
We are going to simply modify this sketch to send a message to the topic /pressed every time the button connected to the Arduino board will be pressed.
Attaching here the resulting modified sketch.
#include <WiFi101.h>
#include <WiFiSSLClient.h>
#include <MQTTClient.h>
int status = WL_IDLE_STATUS;
MQTTClient client;
WiFiSSLClient net;
int buttonPin = 2;
boolean buttonState = false;
boolean oldButtonState = false;
boolean lightStatus=false;
const char* ssid = "***"; // your network SSID (name)
const char* password = "***"; // your network password
const char* userName = "***";
const char* deviceName = "button";
const char* deviceId = "*****************************";
const char* devicePsw = "*****************************";
void setup() {
Serial.begin(9600);
WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
client.begin("mqtt.arduino.cc", 8883, net);
connect();
pinMode(2, INPUT);
}
void connect() {
Serial.print("checking wifi...");
while ( status != WL_CONNECTED) {
Serial.print("Attempting to connect to WPA SSID: ");
Serial.println(ssid);
// Connect to WPA/WPA2 network:
status = WiFi.begin(ssid, password);
// wait 10 seconds for connection:
delay(4000);
}
Serial.println("connecting...");
while (!client.connect(deviceName, deviceId, devicePsw)) {
Serial.print(".");
}
Serial.println("connected!");
}
void loop() {
client.loop();
buttonState = digitalRead(buttonPin);
if (!buttonState && oldButtonState) {
lightStatus = !lightStatus;
if (lightStatus) {
client.publish("/<username>/button/status", "on");
Serial.println("publishing on");
} else {
client.publish("/<username>/button/status", "off");
Serial.println("publishing off");
}
}
oldButtonState = buttonState;
delay(50);
}
void messageReceived(String topic, String payload, char * bytes, unsigned int length) {
Serial.print("incoming: ");
Serial.print(topic);
Serial.print(" - ");
Serial.print(payload);
Serial.println();
}
Now it is time to create our single webpage that respond whenever we click the button.
Start by downloading the base web-app sketch from Github.
In order to test the server locally on your computer you will need to use a local web-server.
You can use Python SimpleHTTPServer for this. Just move to the folder “baseWebApp” inside the repo you downloaded and launch the server:
python -m SimpleHTTPServer 8080
If everything goes fine, you should be able to see the page in a browser at this address: http://0.0.0.0:8080.
Fill in the required fields in the top of the web page with the browser credential you got from cloud.arduino.cc.
It’s important that in the topic field you write the device name you want to subscribe to, followed by the topic. In our case: button/status.
If you press the big button you should see the “on” box turning red and green again according to the “status” of the button.
The basic sketch is based on paho mqtt js client. Check out the code of the myScript.js to see how you can connect to Arduino Cloud from a browser.
var mqttBrokerURI = "wss://mqtt.arduino.cc:9002/";
var userName = "";
var deviceName = "";
var deviceId = "";
var devicePsw = "";
var topic="";
$(document).ready(function() {
console.log (localStorage.getItem("userName"));
$("input[name=userName]").val(localStorage.getItem("userName"));
$("input[name=deviceName]").val(localStorage.getItem("deviceName"));
$("input[name=deviceId]").val(localStorage.getItem("deviceId"));
$("input[name=devicePsw]").val(localStorage.getItem("devicePsw"));
$("input[name=topic]").val(localStorage.getItem("topic"));
$(".monitor").click(function() {
if ($(".monitor .messages").hasClass("hidden")) {
$(".monitor .messages").removeClass("hidden");
} else {
$(".monitor .messages").addClass("hidden");
}
});
});
function connect() {
setProperties();
client = new Paho.MQTT.Client(mqttBrokerURI, deviceName);
// set callback handlers
client.onConnectionLost = onConnectionLost;
client.onMessageArrived = onMessageArrived;
// connect the client
client.connect({
userName: deviceId,
password: devicePsw,
onSuccess: onConnect,
onFailure: onConnectionFail
});
}
function setProperties() {
userName = $("input[name=userName]").val();
deviceName = $("input[name=deviceName]").val();
deviceId = $("input[name=deviceId]").val();
devicePsw = $("input[name=devicePsw]").val();
topic = $("input[name=topic]").val();
localStorage.setItem("userName", userName);
localStorage.setItem("deviceName", deviceName);
localStorage.setItem("deviceId", deviceId);
localStorage.setItem("devicePsw", devicePsw);
localStorage.setItem("topic", topic);
console.log(localStorage.getItem("userName"));
console.log(localStorage.getItem("deviceName"));
console.log(localStorage.getItem("deviceId"));
console.log(localStorage.getItem("devicePsw"));
}
// Create a client instance
// called when the client connects
function onConnect() {
// Once a connection has been made, make a subscription and send a message.
console.log("connected");
client.subscribe("/"+userName+"/"+topic);
console.log("subscribing to "+topic);
}
function onConnectionFail(response) {
// Once a connection has been made, make a subscription and send a message.
console.log("Impossible to connect");
console.log(response);
}
// called when the client loses its connection
function onConnectionLost(responseObject) {
if (responseObject.errorCode !== 0) {
console.log("onConnectionLost:" + responseObject.errorMessage);
}
}
// called when a message arrives
function onMessageArrived(message) {
console.log(message);
$('.messages tr:first').after("<tr><td>" + message.destinationName + "</td><td>" + message.payloadString + "</td></tr>");
$('.megabutton').removeClass('on');
$('.megabutton').removeClass('off');
$('.megabutton').addClass(''+message.payloadString);
$('.megabutton').text(''+message.payloadString);
}
function sendMessage(topic, val) {
console.log("sending " + val + " to " + deviceName + "/" + topic);
message = new Paho.MQTT.Message(val);
message.destinationName = deviceName + "/" + topic;
message.payloadString = val;
client.send(message);
}
Code
Source : One Button to Rule Them All