Arduino Nano Pinout
The Arduino Nano, as the name suggests is a compact, complete and bread-board friendly microcontroller board. The Nano board weighs around 7 grams with dimensions of 4.5 cms to 1.8 cms (L to B). This article discusses about the technical specs most importantly the pinout and functions of each and every pin in the Arduino Nano board.
How different is Arduino Nano?
Arduino Nano has similar functionalities as Arduino Duemilanove but with a different package. The Nano is inbuilt with the ATmega328P microcontroller, same as the Arduino UNO. The main difference between them is that the UNO board is presented in PDIP (Plastic Dual-In-line Package) form with 30 pins and Nano is available in TQFP (plastic quad flat pack) with 32 pins. The extra 2 pins of Arduino Nano serve for the ADC functionalities, while UNO has 6 ADC ports but Nano has 8 ADC ports. The Nano board doesn’t have a DC power jack as other Arduino boards, but instead has a mini-USB port. This port is used for both programming and serial monitoring. The fascinating feature in Nano is that it will choose the strongest power source with its potential difference, and the power source selecting jumper is invalid.
Arduino Nano – Specification
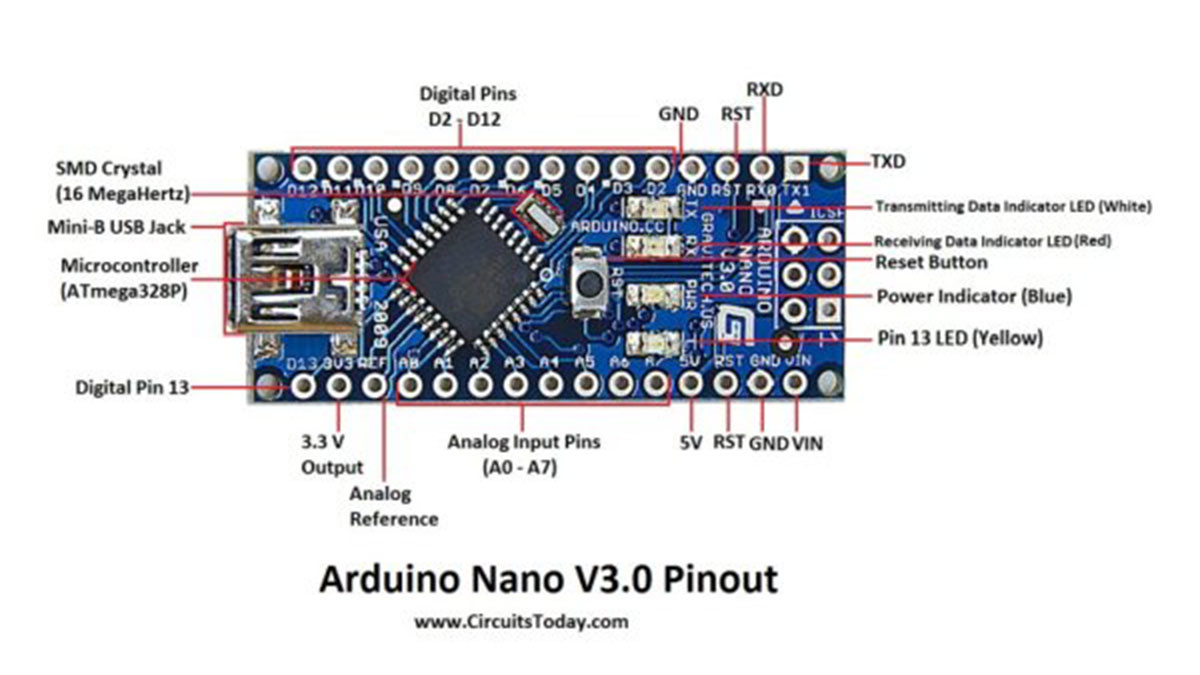
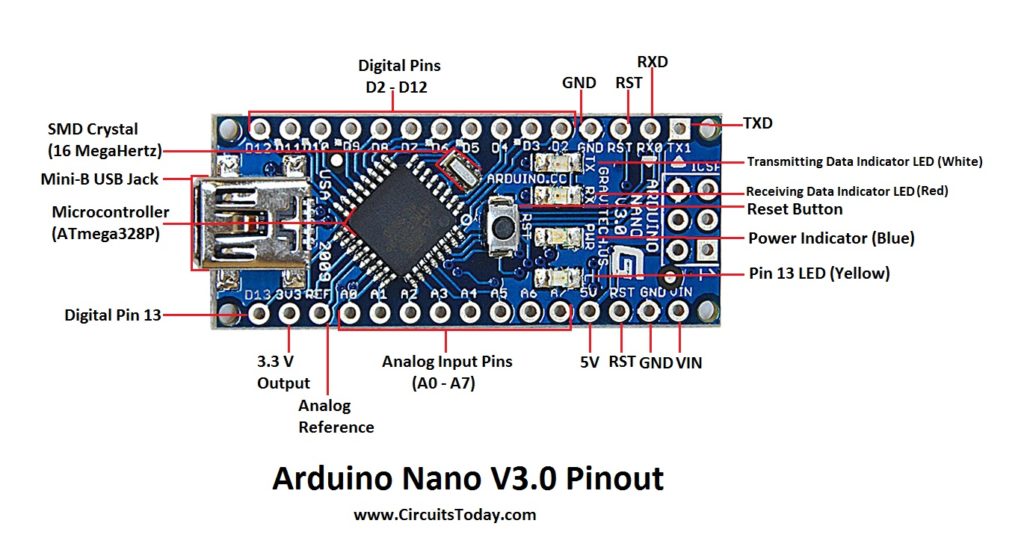
Arduino Nano Pinout Description
Taking this pin-out diagram below as reference, we shall discuss all the functionalities of each and every pin.
Arduino Nano Pinout
We can infer from the image that Arduino Nano got 36 pins in total. We will see all the pins section wise as well as a detailed format at last.
Digital I/O , PWM - 14 Pins For Analog Functions - 9 Pins Power - 7 Pins SPI (Apart from Digital I/O Section) - 3 Pins Reset - 3 Pins ______________________________________________________ TOTAL - 36 Pins
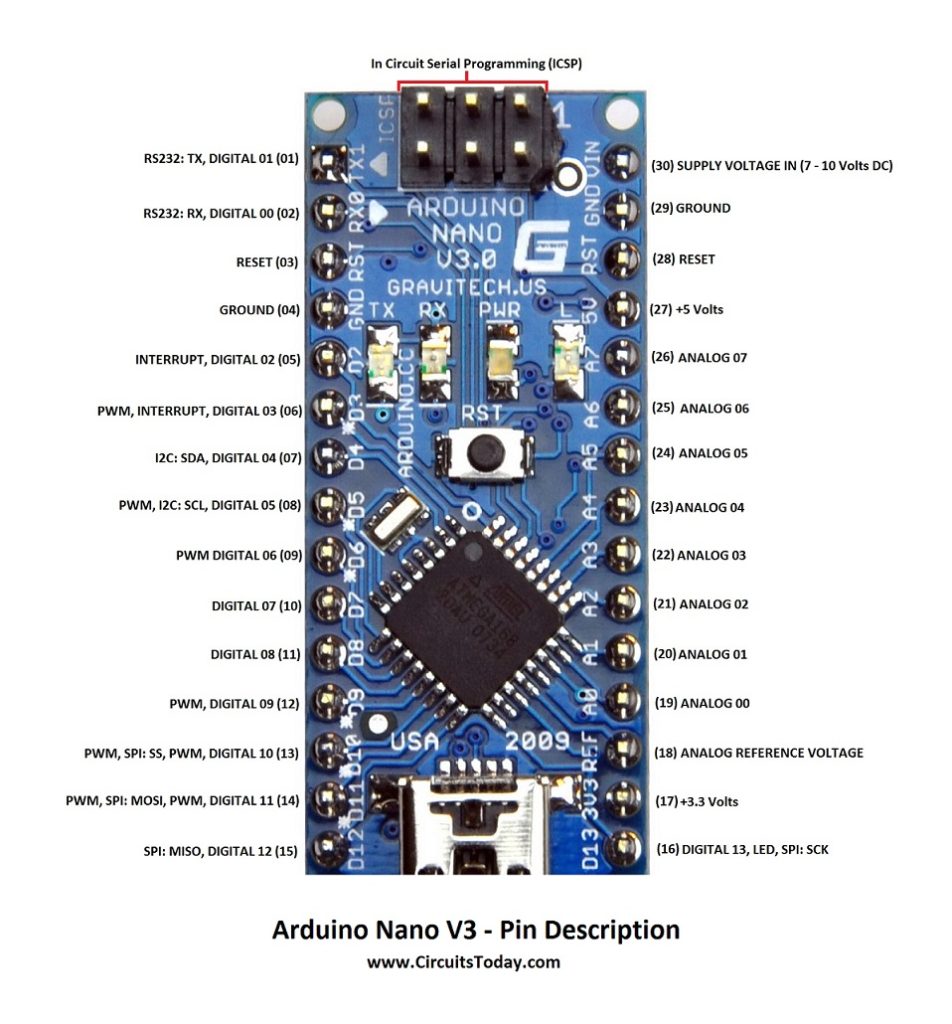
Arduino Nano Pin Description
Arduino Nan0 – Pin Description
Pins 1 to 30
| Arduino Nano Pin | Pin Name | Type | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | D1/TX | I/O | Digital I/O Pin Serial TX Pin |
| 2 | D0/RX | I/O | Digital I/O Pin Serial RX Pin |
| 3 | RESET | Input | Reset ( Active Low) |
| 4 | GND | Power | Supply Ground |
| 5 | D2 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 6 | D3 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 7 | D4 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 8 | D5 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 9 | D6 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 10 | D7 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 11 | D8 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 12 | D9 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 13 | D10 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 14 | D11 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 15 | D12 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 16 | D13 | I/O | Digital I/O Pin |
| 17 | 3V3 | Output | +3.3V Output (from FTDI) |
| 18 | AREF | Input | ADC reference |
| 19 | A0 | Input | Analog Input Channel 0 |
| 20 | A1 | Input | Analog Input Channel 1 |
| 21 | A2 | Input | Analog Input Channel 2 |
| 22 | A3 | Input | Analog Input Channel 3 |
| 23 | A4 | Input | Analog Input Channel 4 |
| 24 | A5 | Input | Analog Input Channel 5 |
| 25 | A6 | Input | Analog Input Channel 6 |
| 26 | A7 | Input | Analog Input Channel 7 |
| 27 | +5V | Output or Input | +5V Output (From On-board Regulator) or +5V (Input from External Power Supply |
| 28 | RESET | Input | Reset ( Active Low) |
| 29 | GND | Power | Supply Ground |
| 30 | VIN | Power | Supply voltage |
ICSP Pins
Arduino Nano Digital Pins
Pins - 1, 2, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, and 16
As mentioned earlier, Arduino Nano has 14 digital I/O pins that can be used either as digital input or output. The pins work with 5V voltage as maximum, i.e., digital high is 5V and digital low is 0V. Each pin can provide or receive a current of 40mA, and has a pull-up resistance of about 20-50k ohms. Each of the 14 digital pins on the Nano pinout can be used as an input or output, using pinMode(), digitalWrite(), and digitalRead() functions.
Other than the digital input and output functions, the digital pins have some additional functionality as well.
Serial Communication Pins
Pins - 1, 2 1 - RX and 2 - TX
These two pins RX- receive and TX- transmit are used for TTL serial data communication. The pins RX and TX are connected to the corresponding pins of the USB-to-TTL Serial chip.
PWM Pins
Pins - 6, 8, 9, 12, 13, and 14
Each of these digital pins provide a Pulse Width Modulation signal of 8-bit resolution. The PWM signal can be generated using analogWrite () function.
External Interrupts
Pins - 5, 6
When we need to provide an external interrupt to other processor or controller we can make use of these pins. These pins can be used to enable interrupts INT0 and INT1 respectively by using the attachInterrupt () function. These pins can be used to trigger three types of interrupts such as interrupt on a low value, a rising or falling edge interrupt and a change in value interrupt.
SPI Pins
Pins - 13, 14, 15, and 16
When you don’t want the data to be transmitted asynchronously you can use these Serial Peripheral Interface pins. These pins support synchronous communication with SCK as the synchronizing clock. Even though the hardware has this feature, the Arduino software doesn’t have this by default. So you have to include a library called SPI Library for using this feature.
LED
Pin - 16
If you remember your first Arduino code, blinking LED, then you’ll definitely came across this Pin16. The pin 16 is being connected to the blinking LED on the board.
Arduino Nano Analog Pins
Pins - 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25, and 26
As mentioned earlier UNO got 6 analog input pins but Arduino Nano has 8 analog inputs (19 to 26), marked A0 through A7. This means you can connect *8 channel analog sensor inputs for processing. Each of these analog pins has a inbuilt ADC of resolution of 1024 bits (so it will give 1024 values). By default, the pins are measured from ground to 5V. If you want the reference voltage to be 0V to 3.3V, we can give 3.3V to AREF pin (18th Pin) by using the analogReference () function.
Similar to digital pins in Nano, analog pins also got some other functions as well.
I2C
Pins 23, 24 as A4 and A5
Since SPI communication also has its disadvantages such as 4 essential pins and limited within a device. For long distance communication we use the I2C protocol. I2C supports multi master and multi slave with only two wires. One for clock (SCL) and another for data (SDA). For using this I2C feature we need to import a library called Wire library.
AREF
Pin 18
As mentioned already the AREF- Analog Reference pin is used as a reference voltage for analog input for the ADC conversion.
Reset
Pin 28
Reset pins in Arduino are active LOW pins which means if we make this pin value as LOW i.e., 0v, it will reset the controller. Usually used to be connected with switches to use as reset button.
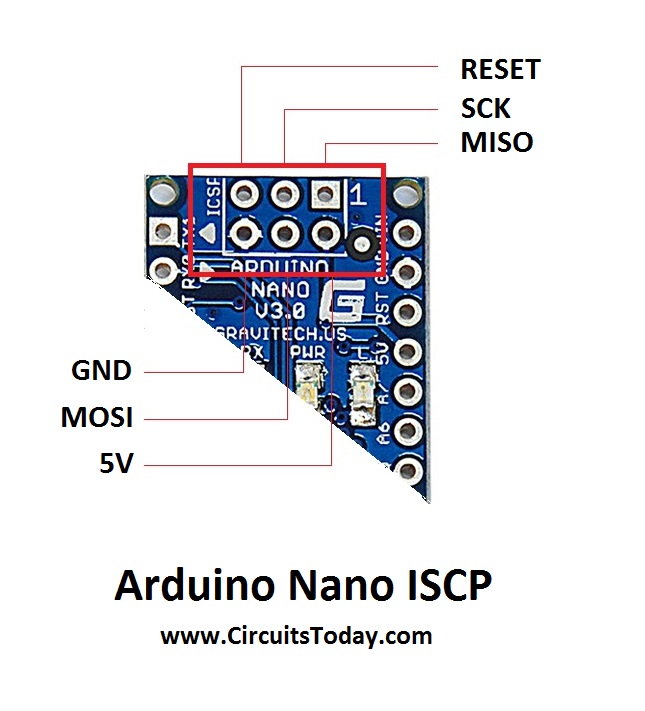
ICSP
Arduino Nano ICSP
ICSP stands for In Circuit Serial Programming, which represents one of the several methods available for programming Arduino boards. Ordinarily, an Arduino bootloader program is used to program an Arduino board, but if the bootloader is missing or damaged, ICSP can be used instead. ICSP can be used to restore a missing or damaged bootloader.
Each ICSP pin usually is cross-connected to another Arduino pin with the same name or function. For example, MISO on Nano’s ICSP header is connected to MISO / digital pin 12 (Pin 15); MOSI on the ISCP header is connected to MOSI / digital pin 11 (Pin 16); and so forth. Note, MISO, MOSI, and SCK pins taken together make up most of an SPI interface.
We can use one Arduino to program another Arduino using this ICSP.
RESET
Pins 3, 28 and 5 in ICSP
Power
Pins 4, 17, 27, 28, 30 and 2 & 6 in ICSP
Source : Arduino Nano Tutorial – Pinout & Schematics