Introduction
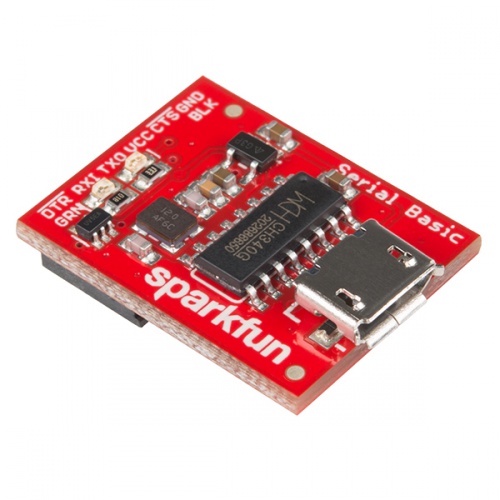
The Serial Basic is an easy to use USB to Serial adapter based on the CH340G IC from WCH. It works with 5V and 3.3V systems and should auto install on most operating systems without the need for additional drivers. It’s a great lower cost option to the extremely popular FTDI Basic.
The Serial Basic uses the CH340G IC to quickly and easily convert serial signals to USB. It works great with all of our products including the Arduino Pro Mini, our GPS modules, cellular modules, and many other devices that uses serial communication.
Suggested Reading
This is an easy board to get started with, but, if you are not sure how serial works or have not used a terminal program before, you may want to checkout the following tutorials.
Serial Basic Overview
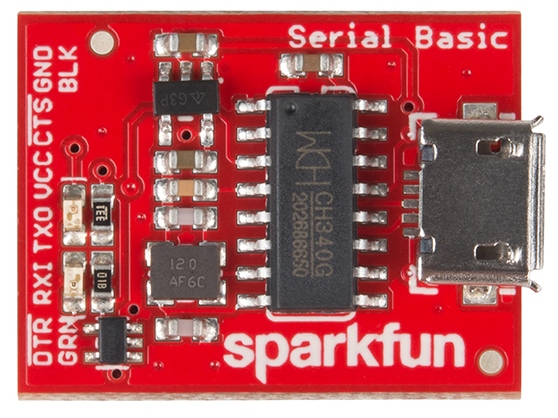
The pinout of the Serial Basic mimics the common DTR/RX/TX/VCC/CTS/GND pinout found on hundreds of FTDI-to-USB derivatives.
| Pin Label | Input/Output | Description |
|---|---|---|
| DTR | Output | Data Terminal Ready, Active Low |
| RXI | Input | Serial Receive |
| TXO | Output | Serial Transmit |
| VCC | Supply Output | Power supply 3.3V or 5V |
| CTS | Input | Clear To Send, Active Low |
| GND | Supply Output | Ground (0V) supply |
Alignment Markers
These GRN and BLK indicators are there to help you align the board properly with products that use this same pinout.
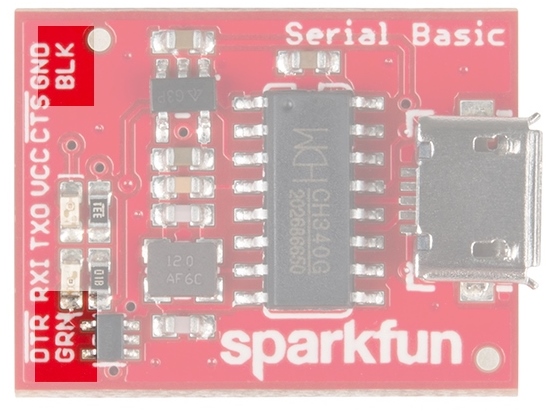
BLK and GRN labels, then you know it will be compatible with the Serial Basic.
Voltage Selection Jumper
There is a jumper on the rear of the board that controls the output voltage on the VCC pin. By default, the board outputs 3.3V and has 3.3V signals. Changing this jumper to 5V will cause the board to output 5V on the VCC pin with 5V signals.
When the jumper is set to 3.3V, the board uses an onboard 3.3V regulator capable of sourcing 600mA. If you attempt to pull more than 600mA, the regulator will go into short-circuit shutdown where it will only output 150mA.
When the jumper is set to 5V, the board will source as much power as your USB port will provide.
LEDs
There are two LEDs on the board connected to TX (Green) and RX (Yellow). This is a quick and handy way to see the serial traffic.
Hardware Test
To connect the board to a computer, you will need a standard A to micro-B USB cable. Plug the micro-B USB cable into a USB port on your computer and the other end into the Serial Basic. Your computer should automatically install the necessary drivers and create a COM port on your computer. If you are prompted for drivers, please see the Installing Drivers section.
The quickest and easiest way to make sure everything is working is to do a TX/RX loop-back. To do this, insert a jumper wire between TX and RX. Anything that is transmitted from the TX pin will be echoed back to the RX pin.
Open your favorite terminal program. Select the COM port that the Serial Basic is assigned to, and connect. When you type a character, you should see each character you type echoed back in the terminal.
Read More: Serial Basic Hookup Guide